What factors contribute to the energy efficiency of a front door?
What contributes to the energy efficiency of a door?
 The material and construction of the door play crucial roles. Here’s a breakdown of what you should consider:
The material and construction of the door play crucial roles. Here’s a breakdown of what you should consider:
Door Material: Different materials offer varying levels of energy efficiency. Generally, wood provides the highest energy efficiency, followed by vinyl, and then glass.
Weatherstripping: This is a flexible foam material that lines the perimeter of the door panel. Combined with a sweep watershed at the bottom of the panel, it helps to resist wind and water infiltration. Outswing front doors may include an additional "rain skirt" for enhanced protection against wind-driven rain.
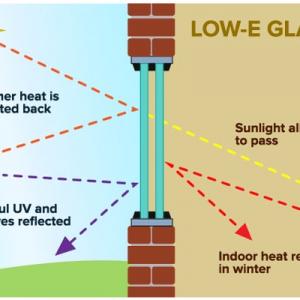
Glass: Doors with glass components can benefit from dual-pane glass, which consists of two sheets of glass with an air space in between. This space can be filled with an argon-gas blend to improve insulation. Additionally, low-emissivity (Low-E) glass coatings are available to minimize energy loss. The choice of coating depends on your climate and specific needs.
Storm Doors: While technically a separate installation from the front door, storm doors provide an additional layer of insulation and protection against the elements, thereby further improving energy efficiency.
By considering these factors—material, weatherstripping, glass type, and storm doors—you can make informed choices to enhance the energy efficiency of your entryway.
How installation plays a critical role in the energy efficiency of a door?
Here’s why proper installation is crucial:
Fit and Alignment: A door must fit snugly into its rough opening in the wall. The rough opening is the space where the door or window is installed. A properly installed door will be level vertically (plumb) and horizontally aligned. Each of the four corners should form a perfect 90-degree angle (square).
Sealing and Insulation: Proper sealing around the door frame is essential to prevent air leaks and drafts. Insulation should be correctly placed between the rough opening and the door frame. This insulation helps to maintain the indoor temperature and prevents energy loss
Weatherstripping: Ensuring that weatherstripping is correctly installed and in good condition further enhances the door’s ability to resist air infiltration and improve energy efficiency.
Hardware and Accessories: The installation of hinges, locks, and any additional accessories should be done securely and with attention to detail. Poorly installed hardware can lead to gaps or misalignment that compromise energy efficiency.
In summary, while the material and construction of a door are important for energy efficiency, proper installation ensures that the door functions optimally by minimizing air leaks, maintaining insulation, and providing a secure fit within the opening. This comprehensive approach ensures that your door contributes effectively to the overall energy efficiency of your home.
How to compare front door performance
If you’re looking to compare the energy efficiency of one front door to another, here are some points to research:
-
What material is the door made of? Wood offers good thermal performance, which is why we use it in our doors. We also add protective cladding that helps keep our doors low-maintenance and high-performing over time.
-
Is the window glass dual pane? Dual-pane glass comes standard on all our windows, including entry door windows. Ours can be ordered with an argon-gas blend in between the panes to further improve insulation.
- Are Low-E coatings available? Low-E coatings come standard on our entry door windows. These coatings are climate specific, so there’s an option that will make your home more comfortable — no matter if you’re seeking to gain solar heating or avoid it.